Navigating Sustainability in Business: Exploring the Triple Bottom Line and Quadruple Bottom Line
In a world increasingly shaped by environmental and social concerns, the traditional bottom line of profit is no longer the sole measure of a company's success. Enter the Triple Bottom Line (TBL) and its more comprehensive counterpart, the Quadruple Bottom Line (QBL). These frameworks provide businesses with a holistic approach to evaluating their performance, going beyond financial metrics to encompass social, environmental, and ethical considerations.
Understanding the Triple Bottom Line (TBL):
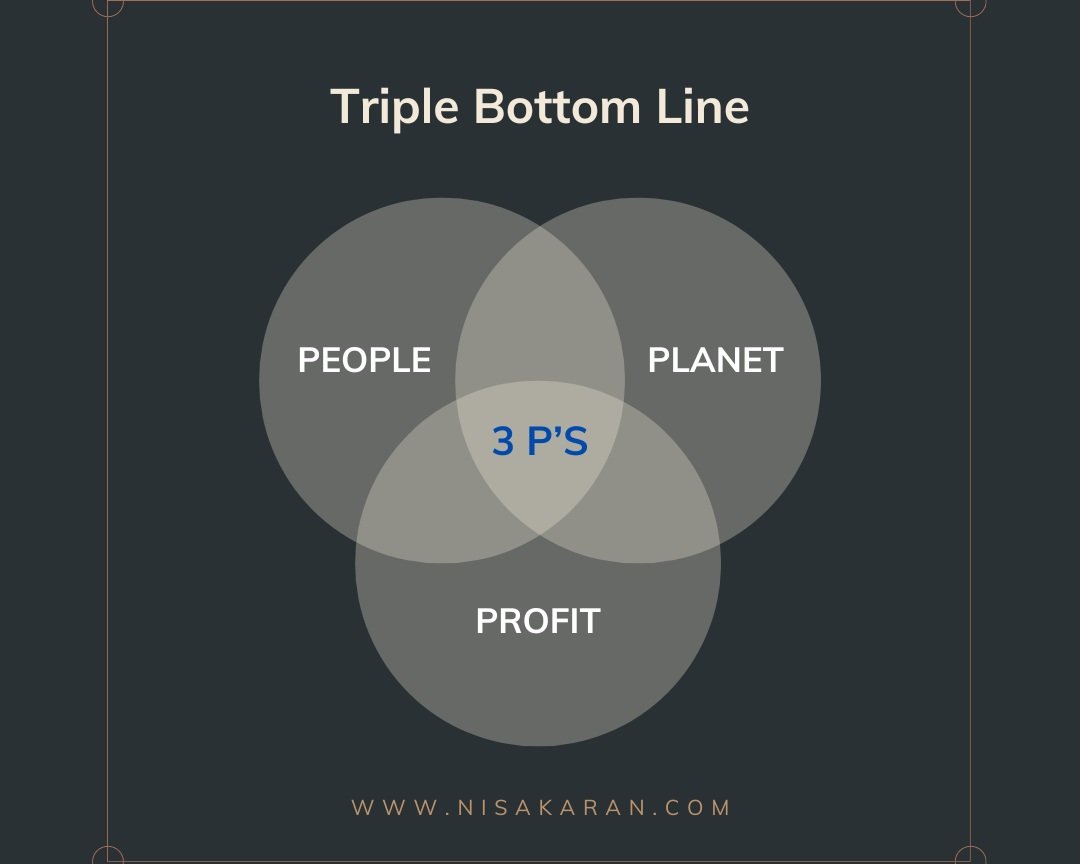
The Triple Bottom Line, coined by John Elkington in 1994, suggests that businesses should assess their success in three dimensions: People, Planet, and Profit. This framework recognizes that economic prosperity is intertwined with social responsibility and environmental stewardship.
1. People: The social dimension of the TBL focuses on the impact a business has on its employees, customers, and the communities in which it operates. Ethical labor practices, diversity and inclusion, and community engagement are essential components.
2. Planet: This dimension addresses a company's environmental footprint. It considers sustainable practices, resource conservation, and efforts to minimize negative environmental impacts. Embracing renewable energy, reducing waste, and adopting eco-friendly initiatives fall under the "Planet" category.
3. Profit: While profit remains a crucial component, the TBL emphasizes responsible financial practices. It encourages businesses to consider the long-term implications of their decisions on both people and the planet, aiming for sustainable profitability.
3 P’s of the Triple Bottom Line
The Evolution to the Quadruple Bottom Line (QBL):
In response to the evolving business landscape, some advocates have expanded the TBL to include a fourth dimension: Governance. The Quadruple Bottom Line introduces the concept that ethical and transparent governance is integral to a company's overall success.
4. Governance: This dimension highlights the importance of ethical leadership, corporate governance, and transparency. Businesses are encouraged to operate with integrity, adhering to ethical principles and fostering accountability at all levels of the organization.
Benefits of the TBL and QBL:
1. Enhanced Corporate Reputation: Embracing a TBL or QBL approach can enhance a company's reputation by showcasing its commitment to social and environmental responsibility.
2. Risk Mitigation: Considering the broader impacts of business decisions helps identify and mitigate potential risks related to environmental, social, or governance issues.
3. Attracting and Retaining Talent: In a socially conscious era, employees increasingly seek employers aligned with their values. Adopting a TBL or QBL approach can attract and retain top talent.
4. Market Opportunities: Consumers are becoming more mindful of their choices, and businesses that align with sustainable values may find new market opportunities and customer loyalty.
5. Long-Term Sustainability: By considering a broader set of factors, businesses can develop strategies that ensure long-term sustainability and resilience in the face of changing economic, social, and environmental landscapes.
4 P’s of the Quadruple Bottom Line
Challenges and Implementation:
While the TBL and QBL offer comprehensive frameworks, implementing them comes with challenges. Companies may face resistance to change, and measuring social and environmental impacts can be complex. However, tools such as sustainability reporting standards and impact assessments can aid in the process.
Conclusion:
As businesses grapple with the evolving expectations of stakeholders, the Triple Bottom Line and Quadruple Bottom Line provide valuable frameworks for navigating the complexities of a sustainable and responsible future. These approaches recognize that success goes beyond financial gain and that businesses must embrace their roles as stewards of people, the planet, and ethical governance to thrive in the long run. The journey toward a more comprehensive understanding of business success is not just a trend; it's a paradigm shift that reflects the values of a global society striving for a better and more sustainable future.